Plot widget fundamentals¶
QwtPlot¶
- class qwt.plot.QwtPlot(*args)[source]¶
A 2-D plotting widget
QwtPlot is a widget for plotting two-dimensional graphs. An unlimited number of plot items can be displayed on its canvas. Plot items might be curves (
qwt.plot_curve.QwtPlotCurve), markers (qwt.plot_marker.QwtPlotMarker), the grid (qwt.plot_grid.QwtPlotGrid), or anything else derived fromQwtPlotItem.A plot can have up to four axes, with each plot item attached to an x- and a y axis. The scales at the axes can be explicitly set (QwtScaleDiv), or are calculated from the plot items, using algorithms (QwtScaleEngine) which can be configured separately for each axis.
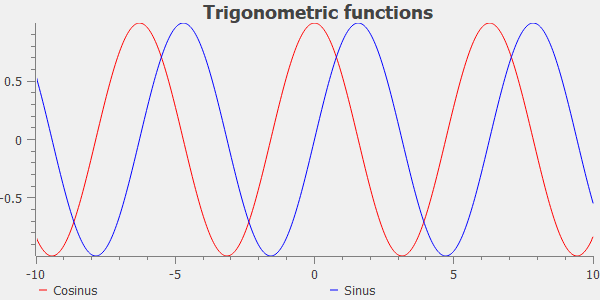
The following example is a good starting point to see how to set up a plot widget:
from qtpy import QtWidgets as QW import qwt import numpy as np app = QW.QApplication([]) x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 500) plot = qwt.QwtPlot("Trigonometric functions") plot.insertLegend(qwt.QwtLegend(), qwt.QwtPlot.BottomLegend) qwt.QwtPlotCurve.make(x, np.cos(x), "Cosinus", plot, linecolor="red", antialiased=True) qwt.QwtPlotCurve.make(x, np.sin(x), "Sinus", plot, linecolor="blue", antialiased=True) plot.resize(600, 300) plot.show()
- class QwtPlot([title=""][, parent=None])¶
- Parameters:
title (str) – Title text
parent (QWidget) – Parent widget
- itemAttached¶
A signal indicating, that an item has been attached/detached
- Parameters:
plotItem – Plot item
on – Attached/Detached
- legendDataChanged¶
A signal with the attributes how to update the legend entries for a plot item.
- Parameters:
itemInfo – Info about a plot item, build from itemToInfo()
data – Attributes of the entries (usually <= 1) for the plot item.
- insertItem(item)[source]¶
Insert a plot item
- Parameters:
item (qwt.plot.QwtPlotItem) – PlotItem
See also
Note
This was a member of QwtPlotDict in older versions.
- removeItem(item)[source]¶
Remove a plot item
- Parameters:
item (qwt.plot.QwtPlotItem) – PlotItem
See also
Note
This was a member of QwtPlotDict in older versions.
- detachItems(rtti=None)[source]¶
Detach items from the dictionary
- Parameters:
rtti (int or None) – In case of QwtPlotItem.Rtti_PlotItem or None (default) detach all items otherwise only those items of the type rtti.
Note
This was a member of QwtPlotDict in older versions.
- itemList(rtti=None)[source]¶
A list of attached plot items.
Use caution when iterating these lists, as removing/detaching an item will invalidate the iterator. Instead you can place pointers to objects to be removed in a removal list, and traverse that list later.
- Parameters:
rtti (int) – In case of QwtPlotItem.Rtti_PlotItem detach all items otherwise only those items of the type rtti.
- Returns:
List of all attached plot items of a specific type. If rtti is None, return a list of all attached plot items.
Note
This was a member of QwtPlotDict in older versions.
- setFlatStyle(state)[source]¶
Set or reset the flatStyle option
If the flatStyle option is set, the plot will be rendered without any margin (scales, canvas, layout).
Enabling this option makes the plot look flat and compact.
The flatStyle option is set to True by default.
- Parameters:
state (bool) – True or False.
See also
- axisWidget(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
- Returns:
Scale widget of the specified axis, or None if axisId is invalid.
- setAxisScaleEngine(axisId, scaleEngine)[source]¶
Change the scale engine for an axis
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
scaleEngine (qwt.scale_engine.QwtScaleEngine) – Scale engine
See also
- axisScaleEngine(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
- Returns:
Scale engine for a specific axis
See also
- axisAutoScale(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
- Returns:
True, if autoscaling is enabled
- axisEnabled(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
- Returns:
True, if a specified axis is enabled
- axisFont(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
- Returns:
The font of the scale labels for a specified axis
- axisMaxMajor(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
- Returns:
The maximum number of major ticks for a specified axis
- axisMaxMinor(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
- Returns:
The maximum number of minor ticks for a specified axis
- axisScaleDiv(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
- Returns:
The scale division of a specified axis
axisScaleDiv(axisId).lowerBound(), axisScaleDiv(axisId).upperBound() are the current limits of the axis scale.
- axisScaleDraw(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
- Returns:
Specified scaleDraw for axis, or NULL if axis is invalid.
- axisStepSize(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
- Returns:
step size parameter value
This doesn’t need to be the step size of the current scale.
- axisMargin(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
- Returns:
Margin in % of the canvas size
See also
- axisInterval(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
- Returns:
The current interval of the specified axis
This is only a convenience function for axisScaleDiv(axisId).interval()
See also
- enableAxis(axisId, tf=True)[source]¶
Enable or disable a specified axis
When an axis is disabled, this only means that it is not visible on the screen. Curves, markers and can be attached to disabled axes, and transformation of screen coordinates into values works as normal.
Only xBottom and yLeft are enabled by default.
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
tf (bool) – True (enabled) or False (disabled)
- invTransform(axisId, pos)[source]¶
Transform the x or y coordinate of a position in the drawing region into a value.
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
pos (int) – position
Warning
The position can be an x or a y coordinate, depending on the specified axis.
- transform(axisId, value)[source]¶
Transform a value into a coordinate in the plotting region
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
value (fload) – Value
- Returns:
X or Y coordinate in the plotting region corresponding to the value.
- setAxisFont(axisId, font)[source]¶
Change the font of an axis
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
font (QFont) – Font
Warning
This function changes the font of the tick labels, not of the axis title.
- setAxisAutoScale(axisId, on=True)[source]¶
Enable autoscaling for a specified axis
This member function is used to switch back to autoscaling mode after a fixed scale has been set. Autoscaling is enabled by default.
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
on (bool) – On/Off
See also
Note
The autoscaling flag has no effect until updateAxes() is executed ( called by replot() ).
- setAxisScale(axisId, min_, max_, stepSize=0)[source]¶
Disable autoscaling and specify a fixed scale for a selected axis.
In updateAxes() the scale engine calculates a scale division from the specified parameters, that will be assigned to the scale widget. So updates of the scale widget usually happen delayed with the next replot.
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
min (float) – Minimum of the scale
max (float) – Maximum of the scale
stepSize (float) – Major step size. If <code>step == 0</code>, the step size is calculated automatically using the maxMajor setting.
- setAxisScaleDiv(axisId, scaleDiv)[source]¶
Disable autoscaling and specify a fixed scale for a selected axis.
The scale division will be stored locally only until the next call of updateAxes(). So updates of the scale widget usually happen delayed with the next replot.
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
scaleDiv (qwt.scale_div.QwtScaleDiv) – Scale division
See also
- setAxisScaleDraw(axisId, scaleDraw)[source]¶
Set a scale draw
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
scaleDraw (qwt.scale_draw.QwtScaleDraw) – Object responsible for drawing scales.
By passing scaleDraw it is possible to extend QwtScaleDraw functionality and let it take place in QwtPlot. Please note that scaleDraw has to be created with new and will be deleted by the corresponding QwtScale member ( like a child object ).
See also
qwt.scale_draw.QwtScaleDraw,qwt.scale_widget.QwtScaleWigdetWarning
The attributes of scaleDraw will be overwritten by those of the previous QwtScaleDraw.
- setAxisLabelAlignment(axisId, alignment)[source]¶
Change the alignment of the tick labels
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
alignment (Qt.Alignment) – Or’d Qt.AlignmentFlags
- setAxisLabelRotation(axisId, rotation)[source]¶
Rotate all tick labels
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
rotation (float) – Angle in degrees. When changing the label rotation, the label alignment might be adjusted too.
See also
setLabelRotation(),setAxisLabelAlignment()
- setAxisLabelAutoSize(axisId, state)[source]¶
Set tick labels automatic size option (default: on)
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
state (bool) – On/off
- setAxisMaxMinor(axisId, maxMinor)[source]¶
Set the maximum number of minor scale intervals for a specified axis
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
maxMinor (int) – Maximum number of minor steps
See also
- setAxisMaxMajor(axisId, maxMajor)[source]¶
Set the maximum number of major scale intervals for a specified axis
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
maxMajor (int) – Maximum number of major steps
See also
- setAxisMargin(axisId, margin)[source]¶
Set the margin of the scale widget
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
margin (float) – Margin in % of the canvas size
See also
- setAxisTitle(axisId, title)[source]¶
Change the title of a specified axis
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis index
title (qwt.text.QwtText or str) – axis title
- updateAxes()[source]¶
Rebuild the axes scales
In case of autoscaling the boundaries of a scale are calculated from the bounding rectangles of all plot items, having the QwtPlotItem.AutoScale flag enabled (QwtScaleEngine.autoScale()). Then a scale division is calculated (QwtScaleEngine.didvideScale()) and assigned to scale widget.
When the scale boundaries have been assigned with setAxisScale() a scale division is calculated (QwtScaleEngine.didvideScale()) for this interval and assigned to the scale widget.
When the scale has been set explicitly by setAxisScaleDiv() the locally stored scale division gets assigned to the scale widget.
The scale widget indicates modifications by emitting a QwtScaleWidget.scaleDivChanged() signal.
updateAxes() is usually called by replot().
- setCanvas(canvas)[source]¶
Set the drawing canvas of the plot widget.
The default canvas is a QwtPlotCanvas.
- Parameters:
canvas (QWidget) – Canvas Widget
See also
- autoRefresh()[source]¶
Replots the plot if
autoReplot()is True.
- setAutoReplot(tf=True)[source]¶
Set or reset the autoReplot option
If the autoReplot option is set, the plot will be updated implicitly by manipulating member functions. Since this may be time-consuming, it is recommended to leave this option switched off and call
replot()explicitly if necessary.The autoReplot option is set to false by default, which means that the user has to call
replot()in order to make changes visible.- Parameters:
tf (bool) – True or False. Defaults to True.
See also
- setTitle(title)[source]¶
Change the plot’s title
- Parameters:
title (str or qwt.text.QwtText) – New title
See also
Change the text the footer
- Parameters:
text (str or qwt.text.QwtText) – New text of the footer
See also
- Returns:
Text of the footer
See also
- Returns:
Footer label widget.
- setPlotLayout(layout)[source]¶
Assign a new plot layout
- Parameters:
layout (qwt.plot_layout.QwtPlotLayout) – Layout
See also
- replot()[source]¶
Redraw the plot
If the autoReplot option is not set (which is the default) or if any curves are attached to raw data, the plot has to be refreshed explicitly in order to make changes visible.
See also
- getCanvasMarginsHint(maps, canvasRect)[source]¶
Calculate the canvas margins
- Parameters:
maps (list) – QwtPlot.axisCnt maps, mapping between plot and paint device coordinates
canvasRect (QRectF) – Bounding rectangle where to paint
Plot items might indicate, that they need some extra space at the borders of the canvas by the QwtPlotItem.Margins flag.
See also
updateCanvasMargins(),getCanvasMarginHint()
- updateCanvasMargins()[source]¶
Update the canvas margins
Plot items might indicate, that they need some extra space at the borders of the canvas by the QwtPlotItem.Margins flag.
- drawCanvas(painter)[source]¶
Redraw the canvas.
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter used for drawing
Warning
drawCanvas calls drawItems what is also used for printing. Applications that like to add individual plot items better overload drawItems()
- drawItems(painter, canvasRect, maps)[source]¶
Redraw the canvas.
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter used for drawing
canvasRect (QRectF) – Bounding rectangle where to paint
maps (list) – QwtPlot.axisCnt maps, mapping between plot and paint device coordinates
Note
Usually canvasRect is contentsRect() of the plot canvas. Due to a bug in Qt this rectangle might be wrong for certain frame styles ( f.e QFrame.Box ) and it might be necessary to fix the margins manually using QWidget.setContentsMargins()
- canvasMap(axisId)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axisId (int) – Axis
- Returns:
Map for the axis on the canvas. With this map pixel coordinates can translated to plot coordinates and vice versa.
See also
- setCanvasBackground(brush)[source]¶
Change the background of the plotting area
Sets brush to QPalette.Window of all color groups of the palette of the canvas. Using canvas().setPalette() is a more powerful way to set these colors.
- Parameters:
brush (QBrush) – New background brush
See also
- axisValid(axis_id)[source]¶
- Parameters:
axis_id (int) – Axis
- Returns:
True if the specified axis exists, otherwise False
- insertLegend(legend, pos=None, ratio=-1)[source]¶
Insert a legend
If the position legend is QwtPlot.LeftLegend or QwtPlot.RightLegend the legend will be organized in one column from top to down. Otherwise the legend items will be placed in a table with a best fit number of columns from left to right.
insertLegend() will set the plot widget as parent for the legend. The legend will be deleted in the destructor of the plot or when another legend is inserted.
Legends, that are not inserted into the layout of the plot widget need to connect to the legendDataChanged() signal. Calling updateLegend() initiates this signal for an initial update. When the application code wants to implement its own layout this also needs to be done for rendering plots to a document ( see QwtPlotRenderer ).
- Parameters:
legend (qwt.legend.QwtAbstractLegend) – Legend
pos (QwtPlot.LegendPosition) – The legend’s position.
ratio (float) – Ratio between legend and the bounding rectangle of title, canvas and axes
Note
For top/left position the number of columns will be limited to 1, otherwise it will be set to unlimited.
Note
The legend will be shrunk if it would need more space than the given ratio. The ratio is limited to ]0.0 .. 1.0]. In case of <= 0.0 it will be reset to the default ratio. The default vertical/horizontal ratio is 0.33/0.5.
- updateLegend(plotItem=None)[source]¶
If plotItem is None, emit QwtPlot.legendDataChanged for all plot item. Otherwise, emit the signal for passed plot item.
- Parameters:
plotItem (qwt.plot.QwtPlotItem) – Plot item
- updateLegendItems(plotItem, legendData)[source]¶
Update all plot items interested in legend attributes
Call QwtPlotItem.updateLegend(), when the QwtPlotItem.LegendInterest flag is set.
- Parameters:
plotItem (qwt.plot.QwtPlotItem) – Plot item
legendData (list) – Entries to be displayed for the plot item ( usually 1 )
See also
QwtPlotItem.LegendInterest(),QwtPlotItem.updateLegend()
- attachItem(plotItem, on)[source]¶
Attach/Detach a plot item
- Parameters:
plotItem (qwt.plot.QwtPlotItem) – Plot item
on (bool) – When true attach the item, otherwise detach it
- print_(printer)[source]¶
Print plot to printer
- Parameters:
printer (QPaintDevice or QPrinter or QSvgGenerator) – Printer
- exportTo(filename, size=(800, 600), size_mm=None, resolution=85, format_=None)[source]¶
Export plot to PDF or image file (SVG, PNG, …)
- Parameters:
filename (str) – Filename
size (tuple) – (width, height) size in pixels
size_mm (tuple) – (width, height) size in millimeters
resolution (int) – Resolution in dots per Inch (dpi)
format (str) – File format (PDF, SVG, PNG, …)
QwtPlotItem¶
- class qwt.plot.QwtPlotItem(title=None, icon=None)[source]¶
Base class for items on the plot canvas
A plot item is “something”, that can be painted on the plot canvas, or only affects the scales of the plot widget. They can be categorized as:
Representator
A “Representator” is an item that represents some sort of data on the plot canvas. The different representator classes are organized according to the characteristics of the data:
qwt.plot_marker.QwtPlotMarker: Represents a point or a horizontal/vertical coordinateqwt.plot_curve.QwtPlotCurve: Represents a series of points
Decorators
A “Decorator” is an item, that displays additional information, that is not related to any data:
Depending on the QwtPlotItem.ItemAttribute flags, an item is included into autoscaling or has an entry on the legend.
Before misusing the existing item classes it might be better to implement a new type of plot item ( don’t implement a watermark as spectrogram ). Deriving a new type of QwtPlotItem primarily means to implement the YourPlotItem.draw() method.
See also
The cpuplot example shows the implementation of additional plot items.
- class QwtPlotItem([title=None])¶
Constructor
- Parameters:
title (qwt.text.QwtText or str) – Title of the item
- attach(plot)[source]¶
Attach the item to a plot.
This method will attach a QwtPlotItem to the QwtPlot argument. It will first detach the QwtPlotItem from any plot from a previous call to attach (if necessary). If a None argument is passed, it will detach from any QwtPlot it was attached to.
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot) – Plot widget
See also
- detach()[source]¶
Detach the item from a plot.
This method detaches a QwtPlotItem from any QwtPlot it has been associated with.
See also
- rtti()[source]¶
Return rtti for the specific class represented. QwtPlotItem is simply a virtual interface class, and base classes will implement this method with specific rtti values so a user can differentiate them.
- Returns:
rtti value
- z()[source]¶
Plot items are painted in increasing z-order.
- Returns:
item z order
See also
setZ(),QwtPlotDict.itemList()
- setZ(z)[source]¶
Set the z value
Plot items are painted in increasing z-order.
- Parameters:
z (float) – Z-value
See also
z(),QwtPlotDict.itemList()
- setTitle(title)[source]¶
Set a new title
- Parameters:
title (qwt.text.QwtText or str) – Title
See also
- setItemAttribute(attribute, on=True)[source]¶
Toggle an item attribute
- Parameters:
attribute (int) – Attribute type
on (bool) – True/False
See also
- testItemAttribute(attribute)[source]¶
Test an item attribute
- Parameters:
attribute (int) – Attribute type
- Returns:
True/False
See also
- setItemInterest(interest, on=True)[source]¶
Toggle an item interest
- Parameters:
attribute (int) – Interest type
on (bool) – True/False
See also
- testItemInterest(interest)[source]¶
Test an item interest
- Parameters:
attribute (int) – Interest type
- Returns:
True/False
See also
- setRenderHint(hint, on=True)[source]¶
Toggle a render hint
- Parameters:
hint (int) – Render hint
on (bool) – True/False
See also
- testRenderHint(hint)[source]¶
Test a render hint
- Parameters:
attribute (int) – Render hint
- Returns:
True/False
See also
- setLegendIconSize(size)[source]¶
Set the size of the legend icon
The default setting is 8x8 pixels
- Parameters:
size (QSize) – Size
See also
- legendIcon(index, size)[source]¶
- Parameters:
index (int) – Index of the legend entry (usually there is only one)
size (QSizeF) – Icon size
- Returns:
Icon representing the item on the legend
The default implementation returns an invalid icon
See also
- setVisible(on)[source]¶
Show/Hide the item
- Parameters:
on (bool) – Show if True, otherwise hide
See also
- itemChanged()[source]¶
Update the legend and call QwtPlot.autoRefresh() for the parent plot.
See also
QwtPlot.legendChanged(),QwtPlot.autoRefresh()
- setAxes(xAxis, yAxis)[source]¶
Set X and Y axis
The item will painted according to the coordinates of its Axes.
- Parameters:
xAxis (int) – X Axis (QwtPlot.xBottom or QwtPlot.xTop)
yAxis (int) – Y Axis (QwtPlot.yLeft or QwtPlot.yRight)
See also
- setAxis(xAxis, yAxis)[source]¶
Set X and Y axis
Warning
setAxis has been removed in Qwt6: please use
setAxes()instead
- setXAxis(axis)[source]¶
Set the X axis
The item will painted according to the coordinates its Axes.
- Parameters:
axis (int) – X Axis (QwtPlot.xBottom or QwtPlot.xTop)
See also
- setYAxis(axis)[source]¶
Set the Y axis
The item will painted according to the coordinates its Axes.
- Parameters:
axis (int) – Y Axis (QwtPlot.yLeft or QwtPlot.yRight)
See also
- boundingRect()[source]¶
- Returns:
An invalid bounding rect: QRectF(1.0, 1.0, -2.0, -2.0)
Note
A width or height < 0.0 is ignored by the autoscaler
- getCanvasMarginHint(xMap, yMap, canvasRect)[source]¶
Calculate a hint for the canvas margin
When the QwtPlotItem::Margins flag is enabled the plot item indicates, that it needs some margins at the borders of the canvas. This is f.e. used by bar charts to reserve space for displaying the bars.
The margins are in target device coordinates ( pixels on screen )
- Parameters:
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps x-values into pixel coordinates.
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps y-values into pixel coordinates.
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the canvas in painter coordinates
- legendData()[source]¶
Return all information, that is needed to represent the item on the legend
QwtLegendData is basically a list of QVariants that makes it possible to overload and reimplement legendData() to return almost any type of information, that is understood by the receiver that acts as the legend.
The default implementation returns one entry with the title() of the item and the legendIcon().
- Returns:
Data, that is needed to represent the item on the legend
See also
- updateLegend(item, data)[source]¶
Update the item to changes of the legend info
Plot items that want to display a legend ( not those, that want to be displayed on a legend ! ) will have to implement updateLegend().
updateLegend() is only called when the LegendInterest interest is enabled. The default implementation does nothing.
- Parameters:
item (qwt.plot.QwtPlotItem) – Plot item to be displayed on a legend
data (list) – Attributes how to display item on the legend
Note
Plot items, that want to be displayed on a legend need to enable the QwtPlotItem.Legend flag and to implement legendData() and legendIcon()
- scaleRect(xMap, yMap)[source]¶
Calculate the bounding scale rectangle of 2 maps
- Parameters:
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps x-values into pixel coordinates.
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps y-values into pixel coordinates.
- Returns:
Bounding scale rect of the scale maps, not normalized
- paintRect(xMap, yMap)[source]¶
Calculate the bounding paint rectangle of 2 maps
- Parameters:
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps x-values into pixel coordinates.
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps y-values into pixel coordinates.
- Returns:
Bounding paint rectangle of the scale maps, not normalized
QwtPlotCanvas¶
- class qwt.plot_canvas.QwtPlotCanvas(plot=None)[source]¶
Canvas of a QwtPlot.
Canvas is the widget where all plot items are displayed
See also
Paint attributes:
QwtPlotCanvas.BackingStore:
Paint double buffered reusing the content of the pixmap buffer when possible.
Using a backing store might improve the performance significantly, when working with widget overlays (like rubber bands). Disabling the cache might improve the performance for incremental paints (using
qwt.plot_directpainter.QwtPlotDirectPainter).QwtPlotCanvas.Opaque:
Try to fill the complete contents rectangle of the plot canvas
When using styled backgrounds Qt assumes, that the canvas doesn’t fill its area completely (f.e because of rounded borders) and fills the area below the canvas. When this is done with gradients it might result in a serious performance bottleneck - depending on the size.
When the Opaque attribute is enabled the canvas tries to identify the gaps with some heuristics and to fill those only.
Warning
Will not work for semitransparent backgrounds
QwtPlotCanvas.HackStyledBackground:
Try to improve painting of styled backgrounds
QwtPlotCanvas supports the box model attributes for customizing the layout with style sheets. Unfortunately the design of Qt style sheets has no concept how to handle backgrounds with rounded corners - beside of padding.
When HackStyledBackground is enabled the plot canvas tries to separate the background from the background border by reverse engineering to paint the background before and the border after the plot items. In this order the border gets perfectly antialiased and you can avoid some pixel artifacts in the corners.
QwtPlotCanvas.ImmediatePaint:
When ImmediatePaint is set replot() calls repaint() instead of update().
See also
replot(),QWidget.repaint(),QWidget.update()
Focus indicators:
QwtPlotCanvas.NoFocusIndicator:
Don’t paint a focus indicator
QwtPlotCanvas.CanvasFocusIndicator:
The focus is related to the complete canvas. Paint the focus indicator using paintFocus()
QwtPlotCanvas.ItemFocusIndicator:
The focus is related to an item (curve, point, …) on the canvas. It is up to the application to display a focus indication using f.e. highlighting.
- class QwtPlotCanvas([plot=None])¶
Constructor
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot) – Parent plot widget
See also
- setPaintAttribute(attribute, on=True)[source]¶
Changing the paint attributes
Paint attributes:
QwtPlotCanvas.BackingStore
QwtPlotCanvas.Opaque
QwtPlotCanvas.HackStyledBackground
QwtPlotCanvas.ImmediatePaint
- Parameters:
attribute (int) – Paint attribute
on (bool) – On/Off
See also
- testPaintAttribute(attribute)[source]¶
Test whether a paint attribute is enabled
- Parameters:
attribute (int) – Paint attribute
- Returns:
True, when attribute is enabled
See also
- setFocusIndicator(focusIndicator)[source]¶
Set the focus indicator
Focus indicators:
QwtPlotCanvas.NoFocusIndicator
QwtPlotCanvas.CanvasFocusIndicator
QwtPlotCanvas.ItemFocusIndicator
- Parameters:
focusIndicator (int) – Focus indicator
See also
- setBorderRadius(radius)[source]¶
Set the radius for the corners of the border frame
- Parameters:
radius (float) – Radius of a rounded corner
See also
- drawBorder(painter)[source]¶
Draw the border of the plot canvas
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
See also
Plot items¶
QwtPlotGrid¶
- class qwt.plot_grid.QwtPlotGrid(title='Grid')[source]¶
A class which draws a coordinate grid
The QwtPlotGrid class can be used to draw a coordinate grid. A coordinate grid consists of major and minor vertical and horizontal grid lines. The locations of the grid lines are determined by the X and Y scale divisions which can be assigned with setXDiv() and setYDiv(). The draw() member draws the grid within a bounding rectangle.
- classmethod make(plot=None, z=None, enablemajor=None, enableminor=None, color=None, width=None, style=None, mincolor=None, minwidth=None, minstyle=None)[source]¶
Create and setup a new QwtPlotGrid object (convenience function).
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot or None) – Plot to attach the curve to
z (float or None) – Z-value
enablemajor (bool or None) – Tuple of two boolean values (x, y) for enabling major grid lines
enableminor (bool or None) – Tuple of two boolean values (x, y) for enabling minor grid lines
color (QColor or str or None) – Pen color for both major and minor grid lines (default: Qt.gray)
width (float or None) – Pen width for both major and minor grid lines (default: 1.0)
style (Qt.PenStyle or None) – Pen style for both major and minor grid lines (default: Qt.DotLine)
mincolor (QColor or str or None) – Pen color for minor grid lines only (default: Qt.gray)
minwidth (float or None) – Pen width for minor grid lines only (default: 1.0)
minstyle (Qt.PenStyle or None) – Pen style for minor grid lines only (default: Qt.DotLine)
See also
- enableX(on)[source]¶
Enable or disable vertical grid lines
- Parameters:
on (bool) – Enable (true) or disable
See also
- enableY(on)[source]¶
Enable or disable horizontal grid lines
- Parameters:
on (bool) – Enable (true) or disable
See also
- enableXMin(on)[source]¶
Enable or disable minor vertical grid lines.
- Parameters:
on (bool) – Enable (true) or disable
See also
- enableYMin(on)[source]¶
Enable or disable minor horizontal grid lines.
- Parameters:
on (bool) – Enable (true) or disable
See also
- setXDiv(scaleDiv)[source]¶
Assign an x axis scale division
- Parameters:
scaleDiv (qwt.scale_div.QwtScaleDiv) – Scale division
- setYDiv(scaleDiv)[source]¶
Assign an y axis scale division
- Parameters:
scaleDiv (qwt.scale_div.QwtScaleDiv) – Scale division
- setPen(*args)[source]¶
Build and/or assign a pen for both major and minor grid lines
- setPen(color, width, style)[source]
Build and assign a pen for both major and minor grid lines
In Qt5 the default pen width is 1.0 ( 0.0 in Qt4 ) what makes it non cosmetic (see QPen.isCosmetic()). This method signature has been introduced to hide this incompatibility.
- Parameters:
color (QColor) – Pen color
width (float) – Pen width
style (Qt.PenStyle) – Pen style
- setPen(pen)[source]
Assign a pen for both major and minor grid lines
- Parameters:
pen (QPen) – New pen
See also
pen(),brush()
- setMajorPen(*args)[source]¶
Build and/or assign a pen for both major grid lines
- setMajorPen(color, width, style)[source]
Build and assign a pen for both major grid lines
In Qt5 the default pen width is 1.0 ( 0.0 in Qt4 ) what makes it non cosmetic (see QPen.isCosmetic()). This method signature has been introduced to hide this incompatibility.
- Parameters:
color (QColor) – Pen color
width (float) – Pen width
style (Qt.PenStyle) – Pen style
- setMajorPen(pen)[source]
Assign a pen for the major grid lines
- Parameters:
pen (QPen) – New pen
See also
majorPen(),setMinorPen(),setPen(),pen(),brush()
- setMinorPen(*args)[source]¶
Build and/or assign a pen for both minor grid lines
- setMinorPen(color, width, style)[source]
Build and assign a pen for both minor grid lines
In Qt5 the default pen width is 1.0 ( 0.0 in Qt4 ) what makes it non cosmetic (see QPen.isCosmetic()). This method signature has been introduced to hide this incompatibility.
- Parameters:
color (QColor) – Pen color
width (float) – Pen width
style (Qt.PenStyle) – Pen style
- setMinorPen(pen)[source]
Assign a pen for the minor grid lines
- Parameters:
pen (QPen) – New pen
See also
minorPen(),setMajorPen(),setPen(),pen(),brush()
- draw(painter, xMap, yMap, canvasRect)[source]¶
Draw the grid
The grid is drawn into the bounding rectangle such that grid lines begin and end at the rectangle’s borders. The X and Y maps are used to map the scale divisions into the drawing region screen.
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – X axis map
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Y axis
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the plot canvas
- updateScaleDiv(xScaleDiv, yScaleDiv)[source]¶
Update the grid to changes of the axes scale division
- Parameters:
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Scale division of the x-axis
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Scale division of the y-axis
See also
updateAxes()
QwtPlotCurve¶
- class qwt.plot_curve.QwtPlotCurve(title=None)[source]¶
A plot item, that represents a series of points
A curve is the representation of a series of points in the x-y plane. It supports different display styles and symbols.
Curve styles:
QwtPlotCurve.NoCurve:
Don’t draw a curve. Note: This doesn’t affect the symbols.
QwtPlotCurve.Lines:
Connect the points with straight lines.
QwtPlotCurve.Sticks:
Draw vertical or horizontal sticks ( depending on the orientation() ) from a baseline which is defined by setBaseline().
QwtPlotCurve.Steps:
Connect the points with a step function. The step function is drawn from the left to the right or vice versa, depending on the QwtPlotCurve::Inverted attribute.
QwtPlotCurve.Dots:
Draw dots at the locations of the data points. Note: This is different from a dotted line (see setPen()), and faster as a curve in QwtPlotCurve::NoStyle style and a symbol painting a point.
QwtPlotCurve.UserCurve:
Styles >= QwtPlotCurve.UserCurve are reserved for derived classes of QwtPlotCurve that overload drawCurve() with additional application specific curve types.
Curve attributes:
QwtPlotCurve.Inverted:
For QwtPlotCurve.Steps only. Draws a step function from the right to the left.
Legend attributes:
QwtPlotCurve.LegendNoAttribute:
QwtPlotCurve tries to find a color representing the curve and paints a rectangle with it.
QwtPlotCurve.LegendShowLine:
If the style() is not QwtPlotCurve.NoCurve a line is painted with the curve pen().
QwtPlotCurve.LegendShowSymbol:
If the curve has a valid symbol it is painted.
QwtPlotCurve.LegendShowBrush:
If the curve has a brush a rectangle filled with the curve brush() is painted.
- class QwtPlotCurve([title=None])¶
Constructor
- Parameters:
title (qwt.text.QwtText or str or None) – Curve title
- classmethod make(xdata=None, ydata=None, title=None, plot=None, z=None, x_axis=None, y_axis=None, style=None, symbol=None, linecolor=None, linewidth=None, linestyle=None, antialiased=False, size=None, finite=None)[source]¶
Create and setup a new QwtPlotCurve object (convenience function).
- Parameters:
xdata – List/array of x values
ydata – List/array of y values
title (qwt.text.QwtText or str or None) – Curve title
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot or None) – Plot to attach the curve to
z (float or None) – Z-value
x_axis (int or None) – curve X-axis (default: QwtPlot.yLeft)
y_axis (int or None) – curve Y-axis (default: QwtPlot.xBottom)
style (int or None) – curve style (QwtPlotCurve.NoCurve, QwtPlotCurve.Lines, QwtPlotCurve.Sticks, QwtPlotCurve.Steps, QwtPlotCurve.Dots, QwtPlotCurve.UserCurve)
symbol (qwt.symbol.QwtSymbol or None) – curve symbol
linecolor (QColor or str or None) – curve line color
linewidth (float or None) – curve line width
linestyle (Qt.PenStyle or None) – curve pen style
antialiased (bool) – if True, enable antialiasing rendering
size (int or None) – size of xData and yData
finite (bool) – if True, keep only finite array elements (remove all infinity and not a number values), otherwise do not filter array elements
- setLegendAttribute(attribute, on=True)[source]¶
Specify an attribute how to draw the legend icon
Legend attributes:
QwtPlotCurve.LegendNoAttribute
QwtPlotCurve.LegendShowLine
QwtPlotCurve.LegendShowSymbol
QwtPlotCurve.LegendShowBrush
- Parameters:
attribute (int) – Legend attribute
on (bool) – On/Off
See also
- testLegendAttribute(attribute)[source]¶
- Parameters:
attribute (int) – Legend attribute
- Returns:
True, when attribute is enabled
See also
- setStyle(style)[source]¶
Set the curve’s drawing style
Valid curve styles:
QwtPlotCurve.NoCurve
QwtPlotCurve.Lines
QwtPlotCurve.Sticks
QwtPlotCurve.Steps
QwtPlotCurve.Dots
QwtPlotCurve.UserCurve
- Parameters:
style (int) – Curve style
See also
- setSymbol(symbol)[source]¶
Assign a symbol
The curve will take the ownership of the symbol, hence the previously set symbol will be delete by setting a new one. If symbol is None no symbol will be drawn.
- Parameters:
symbol (qwt.symbol.QwtSymbol) – Symbol
See also
- setPen(*args)[source]¶
Build and/or assign a pen, depending on the arguments.
- setPen(color, width, style)[source]
Build and assign a pen
In Qt5 the default pen width is 1.0 ( 0.0 in Qt4 ) what makes it non cosmetic (see QPen.isCosmetic()). This method signature has been introduced to hide this incompatibility.
- Parameters:
color (QColor) – Pen color
width (float) – Pen width
style (Qt.PenStyle) – Pen style
- setPen(pen)[source]
Assign a pen
- Parameters:
pen (QPen) – New pen
- setBrush(brush)[source]¶
Assign a brush.
In case of brush.style() != QBrush.NoBrush and style() != QwtPlotCurve.Sticks the area between the curve and the baseline will be filled.
In case not brush.color().isValid() the area will be filled by pen.color(). The fill algorithm simply connects the first and the last curve point to the baseline. So the curve data has to be sorted (ascending or descending).
- Parameters:
brush (QBrush or QColor) – New brush
See also
- directPaint(from_, to)[source]¶
When observing a measurement while it is running, new points have to be added to an existing seriesItem. This method can be used to display them avoiding a complete redraw of the canvas.
Setting plot().canvas().setAttribute(Qt.WA_PaintOutsidePaintEvent, True) will result in faster painting, if the paint engine of the canvas widget supports this feature.
- Parameters:
from (int) – Index of the first point to be painted
to (int) – Index of the last point to be painted
See also
- drawSeries(painter, xMap, yMap, canvasRect, from_, to)[source]¶
Draw an interval of the curve
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps x-values into pixel coordinates.
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps y-values into pixel coordinates.
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the canvas
from (int) – Index of the first point to be painted
to (int) – Index of the last point to be painted. If to < 0 the curve will be painted to its last point.
See also
- drawCurve(painter, style, xMap, yMap, canvasRect, from_, to)[source]¶
Draw the line part (without symbols) of a curve interval.
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
style (int) – curve style, see QwtPlotCurve.CurveStyle
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps x-values into pixel coordinates.
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps y-values into pixel coordinates.
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the canvas
from (int) – Index of the first point to be painted
to (int) – Index of the last point to be painted. If to < 0 the curve will be painted to its last point.
See also
draw(),drawDots(),drawLines(),drawSteps(),drawSticks()
- drawLines(painter, xMap, yMap, canvasRect, from_, to)[source]¶
Draw lines
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps x-values into pixel coordinates.
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps y-values into pixel coordinates.
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the canvas
from (int) – Index of the first point to be painted
to (int) – Index of the last point to be painted. If to < 0 the curve will be painted to its last point.
See also
draw(),drawDots(),drawSteps(),drawSticks()
- drawSticks(painter, xMap, yMap, canvasRect, from_, to)[source]¶
Draw sticks
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps x-values into pixel coordinates.
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps y-values into pixel coordinates.
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the canvas
from (int) – Index of the first point to be painted
to (int) – Index of the last point to be painted. If to < 0 the curve will be painted to its last point.
See also
draw(),drawDots(),drawSteps(),drawLines()
- drawDots(painter, xMap, yMap, canvasRect, from_, to)[source]¶
Draw dots
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps x-values into pixel coordinates.
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps y-values into pixel coordinates.
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the canvas
from (int) – Index of the first point to be painted
to (int) – Index of the last point to be painted. If to < 0 the curve will be painted to its last point.
See also
draw(),drawSticks(),drawSteps(),drawLines()
- drawSteps(painter, xMap, yMap, canvasRect, from_, to)[source]¶
Draw steps
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps x-values into pixel coordinates.
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps y-values into pixel coordinates.
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the canvas
from (int) – Index of the first point to be painted
to (int) – Index of the last point to be painted. If to < 0 the curve will be painted to its last point.
See also
draw(),drawSticks(),drawDots(),drawLines()
- setCurveAttribute(attribute, on=True)[source]¶
Specify an attribute for drawing the curve
Supported curve attributes:
QwtPlotCurve.Inverted
- Parameters:
attribute (int) – Curve attribute
on (bool) – On/Off
See also
- fillCurve(painter, xMap, yMap, canvasRect, polygon)[source]¶
Fill the area between the curve and the baseline with the curve brush
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps x-values into pixel coordinates.
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps y-values into pixel coordinates.
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the canvas
polygon (QPolygonF) – Polygon - will be modified !
See also
- closePolyline(painter, xMap, yMap, polygon)[source]¶
Complete a polygon to be a closed polygon including the area between the original polygon and the baseline.
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps x-values into pixel coordinates.
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps y-values into pixel coordinates.
polygon (QPolygonF) – Polygon to be completed
- drawSymbols(painter, symbol, xMap, yMap, canvasRect, from_, to)[source]¶
Draw symbols
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
symbol (qwt.symbol.QwtSymbol) – Curve symbol
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps x-values into pixel coordinates.
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – Maps y-values into pixel coordinates.
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the canvas
from (int) – Index of the first point to be painted
to (int) – Index of the last point to be painted. If to < 0 the curve will be painted to its last point.
See also
- setBaseline(value)[source]¶
Set the value of the baseline
The baseline is needed for filling the curve with a brush or the Sticks drawing style.
The interpretation of the baseline depends on the orientation(). With Qt.Horizontal, the baseline is interpreted as a horizontal line at y = baseline(), with Qt.Vertical, it is interpreted as a vertical line at x = baseline().
The default value is 0.0.
- Parameters:
value (float) – Value of the baseline
See also
- closestPoint(pos)[source]¶
Find the closest curve point for a specific position
- Parameters:
pos (QPoint) – Position, where to look for the closest curve point
- Returns:
tuple (index, dist)
dist is the distance between the position and the closest curve point. index is the index of the closest curve point, or -1 if none can be found ( f.e when the curve has no points ).
Note
closestPoint() implements a dumb algorithm, that iterates over all points
- legendIcon(index, size)[source]¶
- Parameters:
index (int) – Index of the legend entry (ignored as there is only one)
size (QSizeF) – Icon size
- Returns:
Icon representing the curve on the legend
- setData(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Initialize data with a series data object or an array of points.
- setData(data):
- Parameters:
data (.plot_series.QwtSeriesData) – Series data (e.g. QwtPointArrayData instance)
- setData(xData, yData, [size=None], [finite=True]):
Initialize data with x and y arrays.
This signature was removed in Qwt6 and is temporarily maintained here to ensure compatibility with Qwt5.
Same as setSamples(x, y, [size=None], [finite=True])
- Parameters:
x – List/array of x values
y – List/array of y values
size (int or None) – size of xData and yData
finite (bool) – if True, keep only finite array elements (remove all infinity and not a number values), otherwise do not filter array elements
See also
- setSamples(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Initialize data with an array of points.
- setSamples(data):
- Parameters:
data (.plot_series.QwtSeriesData) – Series data (e.g. QwtPointArrayData instance)
- setSamples(samples):
Same as setData(QwtPointArrayData(samples))
- Parameters:
samples – List/array of points
- setSamples(xData, yData, [size=None], [finite=True]):
Same as setData(QwtPointArrayData(xData, yData, [size=None]))
- Parameters:
xData – List/array of x values
yData – List/array of y values
size (int or None) – size of xData and yData
finite (bool) – if True, keep only finite array elements (remove all infinity and not a number values), otherwise do not filter array elements
See also
QwtPlotMarker¶
- class qwt.plot_marker.QwtPlotMarker(title=None)[source]¶
A class for drawing markers
A marker can be a horizontal line, a vertical line, a symbol, a label or any combination of them, which can be drawn around a center point inside a bounding rectangle.
The setSymbol() member assigns a symbol to the marker. The symbol is drawn at the specified point.
With setLabel(), a label can be assigned to the marker. The setLabelAlignment() member specifies where the label is drawn. All the Align*-constants in Qt.AlignmentFlags (see Qt documentation) are valid. The interpretation of the alignment depends on the marker’s line style. The alignment refers to the center point of the marker, which means, for example, that the label would be printed left above the center point if the alignment was set to Qt.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignTop.
Line styles:
QwtPlotMarker.NoLine: No line
QwtPlotMarker.HLine: A horizontal line
QwtPlotMarker.VLine: A vertical line
QwtPlotMarker.Cross: A crosshair
- classmethod make(xvalue=None, yvalue=None, title=None, label=None, symbol=None, plot=None, z=None, x_axis=None, y_axis=None, align=None, orientation=None, spacing=None, linestyle=None, color=None, width=None, style=None, antialiased=False)[source]¶
Create and setup a new QwtPlotMarker object (convenience function).
- Parameters:
xvalue (float or None) – x position (optional, default: None)
yvalue (float or None) – y position (optional, default: None)
title (qwt.text.QwtText or str or None) – Marker title
label (qwt.text.QwtText or str or None) – Label text
symbol (qwt.symbol.QwtSymbol or None) – New symbol
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot or None) – Plot to attach the curve to
z (float or None) – Z-value
x_axis (int) – curve X-axis (default: QwtPlot.yLeft)
y_axis (int) – curve Y-axis (default: QwtPlot.xBottom)
align (Qt.Alignment or None) – Alignment of the label
orientation (Qt.Orientation or None) – Orientation of the label
spacing (int or None) – Spacing (distance between the position and the label)
linestyle (int) – Line style
color (QColor or str or None) – Pen color
width (float) – Pen width
style (Qt.PenStyle) – Pen style
antialiased (bool) – if True, enable antialiasing rendering
See also
setData(),setPen(),attach()
- setValue(*args)[source]¶
Set Value
- setValue(pos):
- Parameters:
pos (QPointF) – Position
- setValue(x, y):
- Parameters:
x (float) – x position
y (float) – y position
- draw(painter, xMap, yMap, canvasRect)[source]¶
Draw the marker
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
xMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – x Scale Map
yMap (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – y Scale Map
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the canvas in painter coordinates
- drawLines(painter, canvasRect, pos)[source]¶
Draw the lines marker
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the canvas in painter coordinates
pos (QPointF) – Position of the marker, translated into widget coordinates
See also
- drawLabel(painter, canvasRect, pos)[source]¶
Align and draw the text label of the marker
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
canvasRect (QRectF) – Contents rectangle of the canvas in painter coordinates
pos (QPointF) – Position of the marker, translated into widget coordinates
See also
- setLineStyle(style)[source]¶
Set the line style
- Parameters:
style (int) – Line style
Line styles:
QwtPlotMarker.NoLine: No line
QwtPlotMarker.HLine: A horizontal line
QwtPlotMarker.VLine: A vertical line
QwtPlotMarker.Cross: A crosshair
See also
- setSymbol(symbol)[source]¶
Assign a symbol
- Parameters:
symbol (qwt.symbol.QwtSymbol) – New symbol
See also
- setLabel(label)[source]¶
Set the label
- Parameters:
label (qwt.text.QwtText or str) – Label text
See also
- setLabelAlignment(align)[source]¶
Set the alignment of the label
In case of QwtPlotMarker.HLine the alignment is relative to the y position of the marker, but the horizontal flags correspond to the canvas rectangle. In case of QwtPlotMarker.VLine the alignment is relative to the x position of the marker, but the vertical flags correspond to the canvas rectangle.
In all other styles the alignment is relative to the marker’s position.
- Parameters:
align (Qt.Alignment) – Alignment
See also
- setLabelOrientation(orientation)[source]¶
Set the orientation of the label
When orientation is Qt.Vertical the label is rotated by 90.0 degrees (from bottom to top).
- Parameters:
orientation (Qt.Orientation) – Orientation of the label
See also
- setSpacing(spacing)[source]¶
Set the spacing
When the label is not centered on the marker position, the spacing is the distance between the position and the label.
- Parameters:
spacing (int) – Spacing
See also
- setLinePen(*args)[source]¶
Build and/or assigna a line pen, depending on the arguments.
- setLinePen(color, width, style)[source]
Build and assign a line pen
In Qt5 the default pen width is 1.0 ( 0.0 in Qt4 ) what makes it non cosmetic (see QPen.isCosmetic()). This method signature has been introduced to hide this incompatibility.
- Parameters:
color (QColor) – Pen color
width (float) – Pen width
style (Qt.PenStyle) – Pen style
- setLinePen(pen)[source]
Specify a pen for the line.
- Parameters:
pen (QPen) – New pen
See also
pen(),brush()
Additional plot features¶
QwtLegend¶
- class qwt.legend.QwtLegendData[source]¶
Attributes of an entry on a legend
QwtLegendData is an abstract container ( like QAbstractModel ) to exchange attributes, that are only known between to the plot item and the legend.
By overloading QwtPlotItem.legendData() any other set of attributes could be used, that can be handled by a modified ( or completely different ) implementation of a legend.
See also
Note
The stockchart example implements a legend as a tree with checkable items
- hasRole(role)[source]¶
- Parameters:
role (int) – Attribute role
- Returns:
True, when the internal map has an entry for role
- setValue(role, data)[source]¶
Set an attribute value
- Parameters:
role (int) – Attribute role
data (QVariant) – Attribute value
See also
- class qwt.legend.QwtLegendLabel(parent=None)[source]¶
A widget representing something on a QwtLegend.
- setData(legendData)[source]¶
Set the attributes of the legend label
- Parameters:
legendData (QwtLegendData) – Attributes of the label
See also
- setText(text)[source]¶
Set the text to the legend item
- Parameters:
text (qwt.text.QwtText) – Text label
See also
text()
- setItemMode(mode)[source]¶
Set the item mode. The default is QwtLegendData.ReadOnly.
- Parameters:
mode (int) – Item mode
See also
- setIcon(icon)[source]¶
Assign the icon
- Parameters:
icon (QPixmap) – Pixmap representing a plot item
See also
- setSpacing(spacing)[source]¶
Change the spacing between icon and text
- Parameters:
spacing (int) – Spacing
See also
- class qwt.legend.QwtLegend(parent=None)[source]¶
The legend widget
The QwtLegend widget is a tabular arrangement of legend items. Legend items might be any type of widget, but in general they will be a QwtLegendLabel.
See also
:py:class`qwt.legend.QwtLegendLabel`, :py:class`qwt.plot.QwtPlotItem`, :py:class`qwt.plot.QwtPlot`
- class QwtLegend([parent=None])¶
Constructor
- Parameters:
parent (QWidget) – Parent widget
- clicked¶
A signal which is emitted when the user has clicked on a legend label, which is in QwtLegendData.Clickable mode.
- Parameters:
itemInfo – Info for the item item of the selected legend item
index – Index of the legend label in the list of widgets that are associated with the plot item
Note
Clicks are disabled as default
- checked¶
A signal which is emitted when the user has clicked on a legend label, which is in QwtLegendData.Checkable mode
- Parameters:
itemInfo – Info for the item of the selected legend label
index – Index of the legend label in the list of widgets that are associated with the plot item
on – True when the legend label is checked
Note
Clicks are disabled as default
- setMaxColumns(numColumns)[source]¶
Set the maximum number of entries in a row
F.e when the maximum is set to 1 all items are aligned vertically. 0 means unlimited
- Parameters:
numColumns (int) – Maximum number of entries in a row
See also
maxColumns(),QwtDynGridLayout.setMaxColumns()
- maxColumns()[source]¶
- Returns:
Maximum number of entries in a row
See also
setMaxColumns(),QwtDynGridLayout.maxColumns()
- setDefaultItemMode(mode)[source]¶
Set the default mode for legend labels
Legend labels will be constructed according to the attributes in a QwtLegendData object. When it doesn’t contain a value for the QwtLegendData.ModeRole the label will be initialized with the default mode of the legend.
- Parameters:
mode (int) – Default item mode
See also
itemMode(),QwtLegendData.value(),QwtPlotItem::legendData()… note:
Changing the mode doesn't have any effect on existing labels.
- contentsWidget()[source]¶
The contents widget is the only child of the viewport of the internal QScrollArea and the parent widget of all legend items.
- Returns:
Container widget of the legend items
- updateLegend(itemInfo, data)[source]¶
Update the entries for an item
- Parameters:
itemInfo (QVariant) – Info for an item
data (list) – Default item mode
- createWidget(data)[source]¶
Create a widget to be inserted into the legend
The default implementation returns a QwtLegendLabel.
- Parameters:
data (QwtLegendData) – Attributes of the legend entry
- Returns:
Widget representing data on the legend
… note:
updateWidget() will called soon after createWidget() with the same attributes.
- updateWidget(widget, data)[source]¶
Update the widget
- Parameters:
widget (QWidget) – Usually a QwtLegendLabel
data (QwtLegendData) – Attributes to be displayed
See also
… note:
When widget is no QwtLegendLabel updateWidget() does nothing.
- heightForWidth(width)[source]¶
- Parameters:
width (int) – Width
- Returns:
The preferred height, for a width.
- eventFilter(object_, event)[source]¶
Handle QEvent.ChildRemoved andQEvent.LayoutRequest events for the contentsWidget().
- Parameters:
object (QObject) – Object to be filtered
event (QEvent) – Event
- Returns:
Forwarded to QwtAbstractLegend.eventFilter()
- renderLegend(painter, rect, fillBackground)[source]¶
Render the legend into a given rectangle.
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
rect (QRectF) – Bounding rectangle
fillBackground (bool) – When true, fill rect with the widget background
- renderItem(painter, widget, rect, fillBackground)[source]¶
Render a legend entry into a given rectangle.
- Parameters:
painter (QPainter) – Painter
widget (QWidget) – Widget representing a legend entry
rect (QRectF) – Bounding rectangle
fillBackground (bool) – When true, fill rect with the widget background
- legendWidgets(itemInfo)[source]¶
List of widgets associated to a item
- Parameters:
itemInfo (QVariant) – Info about an item
Color maps¶
QwtColorMap¶
- class qwt.color_map.QwtColorMap(format_=None)[source]¶
QwtColorMap is used to map values into colors.
For displaying 3D data on a 2D plane the 3rd dimension is often displayed using colors, like f.e in a spectrogram.
Each color map is optimized to return colors for only one of the following image formats:
QImage.Format_Indexed8
QImage.Format_ARGB32
- class QwtColorMap(format_)¶
- Parameters:
format (int) – Preferred format of the color map (
QwtColorMap.RGBorQwtColorMap.Indexed)
See also
qwt.QwtScaleWidget- color(interval, value)[source]¶
Map a value into a color
- Parameters:
interval (qwt.interval.QwtInterval) – valid interval for value
value (float) – value
- Returns:
the color corresponding to value
Warning
This method is slow for Indexed color maps. If it is necessary to map many values, its better to get the color table once and find the color using colorIndex().
- colorTable(interval)[source]¶
Build and return a color map of 256 colors
- Parameters:
interval (qwt.interval.QwtInterval) – range for the values
- Returns:
a color table, that can be used for a QImage
The color table is needed for rendering indexed images in combination with using colorIndex().
QwtLinearColorMap¶
- class qwt.color_map.QwtLinearColorMap(*args)[source]¶
Build a linear color map with two stops.
- class QwtLinearColorMap(format_)¶
Build a color map with two stops at 0.0 and 1.0. The color at 0.0 is Qt.blue, at 1.0 it is Qt.yellow.
- Parameters:
format (int) – Preferred format of the color map (
QwtColorMap.RGBorQwtColorMap.Indexed)
- QwtLinearColorMap(color1, color2, [format_=QwtColorMap.RGB]):
Build a color map with two stops at 0.0 and 1.0.
- Parameters:
color1 (QColor) – color at 0.
color2 (QColor) – color at 1.
format (int) – Preferred format of the color map (
QwtColorMap.RGBorQwtColorMap.Indexed)
- QwtLinearColorMap.setMode(mode)[source]¶
Set the mode of the color map
- Parameters:
mode (int) –
QwtLinearColorMap.FixedColorsorQwtLinearColorMap.ScaledColors
FixedColors means the color is calculated from the next lower color stop. ScaledColors means the color is calculated by interpolating the colors of the adjacent stops.
QwtAlphaColorMap¶
QwtPlotRenderer¶
- class qwt.plot_renderer.QwtPlotRenderer(parent=None)[source]¶
Renderer for exporting a plot to a document, a printer or anything else, that is supported by QPainter/QPaintDevice
Discard flags:
QwtPlotRenderer.DiscardNone: Render all components of the plot
QwtPlotRenderer.DiscardBackground: Don’t render the background of the plot
QwtPlotRenderer.DiscardTitle: Don’t render the title of the plot
QwtPlotRenderer.DiscardLegend: Don’t render the legend of the plot
QwtPlotRenderer.DiscardCanvasBackground: Don’t render the background of the canvas
QwtPlotRenderer.DiscardFooter: Don’t render the footer of the plot
QwtPlotRenderer.DiscardCanvasFrame: Don’t render the frame of the canvas
Note
The QwtPlotRenderer.DiscardCanvasFrame flag has no effect when using style sheets, where the frame is part of the background
Layout flags:
QwtPlotRenderer.DefaultLayout: Use the default layout as on screen
QwtPlotRenderer.FrameWithScales: Instead of the scales a box is painted around the plot canvas, where the scale ticks are aligned to.
- setDiscardFlag(flag, on=True)[source]¶
Change a flag, indicating what to discard from rendering
- Parameters:
flag (int) – Flag to change
on (bool) – On/Off
See also
- testDiscardFlag(flag)[source]¶
- Parameters:
flag (int) – Flag to be tested
- Returns:
True, if flag is enabled.
See also
- setDiscardFlags(flags)[source]¶
Set the flags, indicating what to discard from rendering
- Parameters:
flags (int) – Flags
See also
- setLayoutFlag(flag, on=True)[source]¶
Change a layout flag
- Parameters:
flag (int) – Flag to change
See also
- testLayoutFlag(flag)[source]¶
- Parameters:
flag (int) – Flag to be tested
- Returns:
True, if flag is enabled.
See also
- renderDocument(plot, filename, sizeMM=(300, 200), resolution=85, format_=None)[source]¶
Render a plot to a file
The format of the document will be auto-detected from the suffix of the file name.
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot) – Plot widget
fileName (str) – Path of the file, where the document will be stored
sizeMM (QSizeF) – Size for the document in millimeters
resolution (int) – Resolution in dots per Inch (dpi)
- renderTo(plot, dest)[source]¶
Render a plot to a file
Supported formats are:
pdf: Portable Document Format PDF
ps: Postcript
svg: Scalable Vector Graphics SVG
all image formats supported by Qt, see QImageWriter.supportedImageFormats()
Scalable vector graphic formats like PDF or SVG are superior to raster graphics formats.
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot) – Plot widget
dest – QPaintDevice, QPrinter or QSvgGenerator instance
See also
render(),qwt.painter.QwtPainter.setRoundingAlignment()
- render(plot, painter, plotRect)[source]¶
Paint the contents of a QwtPlot instance into a given rectangle.
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot) – Plot to be rendered
painter (QPainter) – Painter
format (str) – Format for the document
plotRect (QRectF) – Bounding rectangle
See also
renderDocument(),renderTo(),qwt.painter.QwtPainter.setRoundingAlignment()
- renderTitle(plot, painter, rect)[source]¶
Render the title into a given rectangle.
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot) – Plot widget
painter (QPainter) – Painter
rect (QRectF) – Bounding rectangle
Render the footer into a given rectangle.
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot) – Plot widget
painter (QPainter) – Painter
rect (QRectF) – Bounding rectangle
- renderLegend(plot, painter, rect)[source]¶
Render the legend into a given rectangle.
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot) – Plot widget
painter (QPainter) – Painter
rect (QRectF) – Bounding rectangle
- renderScale(plot, painter, axisId, startDist, endDist, baseDist, rect)[source]¶
Paint a scale into a given rectangle. Paint the scale into a given rectangle.
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot) – Plot widget
painter (QPainter) – Painter
axisId (int) – Axis
startDist (int) – Start border distance
endDist (int) – End border distance
baseDist (int) – Base distance
rect (QRectF) – Bounding rectangle
- renderCanvas(plot, painter, canvasRect, maps)[source]¶
Render the canvas into a given rectangle.
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot) – Plot widget
painter (QPainter) – Painter
rect (QRectF) – Bounding rectangle
maps (qwt.scale_map.QwtScaleMap) – mapping between plot and paint device coordinates
- buildCanvasMaps(plot, canvasRect)[source]¶
Calculated the scale maps for rendering the canvas
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot) – Plot widget
canvasRect (QRectF) – Target rectangle
- Returns:
Calculated scale maps
- exportTo(plot, documentname, sizeMM=None, resolution=85)[source]¶
Execute a file dialog and render the plot to the selected file
- Parameters:
plot (qwt.plot.QwtPlot) – Plot widget
documentName (str) – Default document name
sizeMM (QSizeF) – Size for the document in millimeters
resolution (int) – Resolution in dots per Inch (dpi)
- Returns:
True, when exporting was successful
See also
